42 reading labels for sodium
How to Read Salt Labels | Cooking Light For the consumer, the tricky part is that there are four claims. Two apply when a company is comparing their food to a loosely defined fully salted version. One refers to a specific sodium level, another to whether salt has been added. Bottom line: The amount of sodium per serving (found on the back label) is critical. How do you read a food label for salt / sodium? - Irish Kidney Diet If the salt content is not available on a label you can calculate it from the sodium content using the following: Sodium x 2.5 = salt content or Salt ÷ 2.5 = sodium content If you have kidney disease a good goal for sodium intake is 2300 mg of sodium or 6g salt per day.
Understanding Food Nutrition Labels | American Heart Association 1 - Start with the serving information at the top. This will tell you the size of a single serving and the total number of servings per container (package). 2 - Next, check total calories per serving and container. Pay attention to the calories per serving and how many calories you're really consuming if you eat the whole package.

Reading labels for sodium
Sodium: Look at the Label Sodium: Look at the Label Over 70% of dietary sodium comes from eating packaged and prepared foods Sodium and Health Diets higher in sodium are associated with an increased risk of developing How to Read Labels for a Low Sodium Diet - Salt Sanity Sodium Alginate You may find sodium alginate on the ingredient labels in dairy products like yogurt and ice cream where it's used as a stabilizer. It's used to thicken puddings and jams, prevent moisture loss in meats, and to emulsify salad dressings and beverages. Sodium Citrate How To Read Food and Beverage Labels - National Institute on Aging Reading food labels can help you make smart food choices. Learn how to read and understand the product date, ingredient list, and Nutrition Facts label. ... Most older adults exceed the recommended limits for saturated fats, sodium, and added sugars. Compare and choose foods to get less than 100% DV of these each day, making sure to adjust for ...
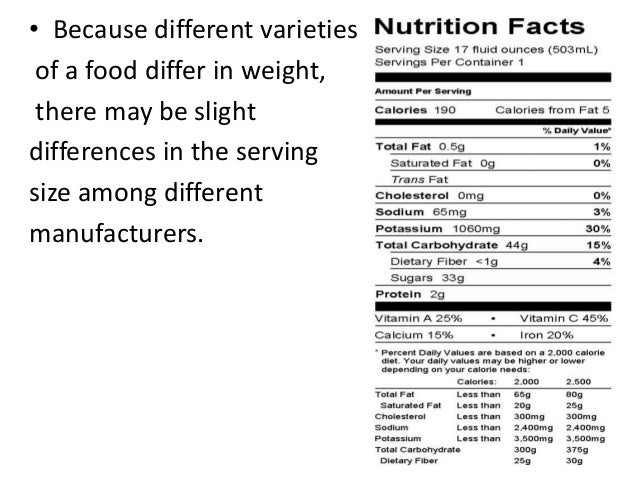
Reading labels for sodium. PDF Read the Nutrition Facts Label for Sodium! - NHLBI, NIH Sodium 125mg 5% Total Carbohydrate 9g 3% Dietary Fiber 3g 12% Sugars 4g Protein 2g Vitamin A 35% • Vitamin C 6% Calcium 2% • Iron 2% Read the Nutrition Facts Label for Sodium! Nutrition Facts labels tell you what you need to know about choosing foods that are lower in sodium. Here is a Nutrition Facts label for frozen peas and carrots ... PDF Reading Food Labels to Look for Sodium sodium-free, salt-free or no sodium less than 5 mg of sodium and no sodium chloride in ingredients very low sodium 35 mg or less of sodium no added salt or unsalted no salt added to the product during processing (this is not a sodium-free product) low sodium 140 mg or less of sodium reduced or less sodium at least 25 percent less sodium than the … Sodium on the Nutrition Facts Label | FDA FDA's Education Materials Sodium in Your Diet Fact Sheet A printable backgrounder that offers the basics on sodium's health effects, easy how-to's for using the Nutrition Facts label to reduce... PDF Controlling Sodium and Reading Labels When You Shop When selecting processed items, read labels to limit the sodium from food and beverages. A low-sodium nutrition plan usually limits dietary sodium to 1,500-2,000 milligrams (mg) per day. Select more 'Low Sodium' foods with 140 mg of sodium or less per servingand limit 'High Sodium' foods with more than 300 mg of sodium per serving.
10 Best Low-Sodium Salad Dressings in 2022 (Registered ... Jun 21, 2022 · Salad dressings can be a fun way to add flavor to your salads and raw vegetables. But, these food products can also add extra salt to your diet. If you need or want to watch your daily salt intake, low-sodium salad dressings can help!Our 10 best list provides an overview of various types of low-sodium salad dressings, including our number one choice, Yo Mama's Honey Balsamic. PDF Reading Food Labels for Sodium (Salt) - Western Health Reading Food Labels for Sodium (Salt) You will find the Nutrition Facts box on most packaged food products. The Percent Daily ... What the Label Says What it Means Free of sodium or salt - "salt-free", "without salt", "contains no sodium" Contains less than 5 mg of sodium or salt per Label Reading for Sodium - Kidney Community Kitchen So if a product has 10% sodium - you should count it as 15%. If a product has 8% sodium you should count it as 12%. This is probably the quickest way to convert when reading a label. It will give you a percentage of a 1600mg sodium per day diet - which is a whole lot better than 2400mg. Here's a simple chart: Keys To Mastering The Low Sodium Life - Reading Nutrition Labels The American Heart Association has established that 1500 mg. daily intake of sodium is a healthy standard. Most Americans consume over 3400 mg. daily. Food labels cannot claim a product is "healthy" if it has more than 480 mg of sodium per labeled serving (for individual foods) or more than 600 mg of sodium per labeled serving for meals ...
How to Convert Salt to Sodium | Ideal Nutrition Aug 02, 2021 · What Is the Difference Between Salt and Sodium? Salt is technically 40% sodium and 60% chloride. This is why salt is referred to as sodium chloride (NaCl). To be overly specific, it has a 1:1 ratio of sodium and chloride ions, but the molar masses are 22.99g/mol and 35.45g/mol respectively which explains why salt is 40% sodium and 60% chloride. What Sodium Labels Mean: A Guide to Decoding Sodium Labels Reduced (or Less) Sodium: This label means that the sodium level in the product has been reduced by 25 percent per serving from the original or a competitor's product. And if that product started with over 500mg sodium per serving, then you're still talking about 375mg of sodium per serving. Label reading 101 - Healthy Food Guide Step 1: Check front-of-pack claims. Manufacturers often use clever wording like 'low in salt' and '97% fat free', but there are lots of rules surrounding nutrition claims. For instance, a 'low-salt' food must have no more than 120mg of sodium per 100g. A food claiming to be '97% fat free' must have a maximum of three per cent fat. How to Read Sodium Percentages on Food Packages - SF Gate Learning how to read sodium percentages on nutrition labels helps ensure a healthy sodium intake below the daily recommended intake. Recommended Daily Intake (RDI) The 2010 Dietary Guidelines recommends that adults consume less than 2,300 milligrams of sodium per day. However, people with certain risk factors or health conditions should consume ...
Reading Food Labels | ADA - American Diabetes Association Put food labels to work. The Nutrition Facts labels on foods are really the key to making the best choices. We'll cover the basics so that these labels make shopping easier for you. You've heard it all. From carb-free to low-carb, to whole and empty carbs, it's hard to know what it all means. Blood sugar highs and lows aren't always ...
How to Decode Salt on Food Labels: Low Sodium vs Reduced Sodium vs ... Reduced Sodium. These foods have at least 25% less sodium than their original version. "Light in sodium" or "lightly salted" items are reduced by 50%. Unlike low sodium foods, reduced sodium foods can still be swimming in sodium. (One reduced-sodium soup we saw packs 660 mg per serving!) Keep an eye out for reduced sodium soups, reduced ...
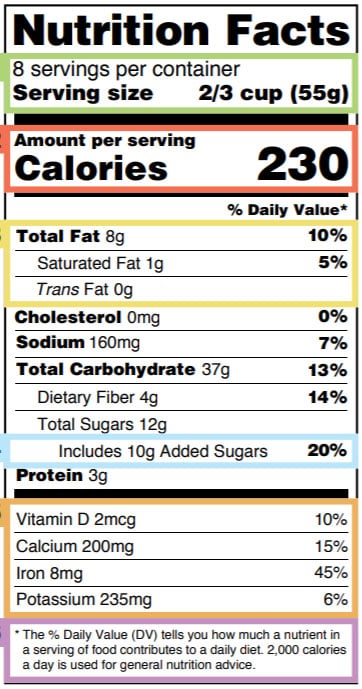
Sodium and Food Labels | Sutter Health It's important to note that all nutritional labels list amounts of nutrients per serving. This item, for example, lists 16 servings in the entire container. The sodium level is 120 mg for one serving. That means if you drink the entire container, you'll get 1,920 mg sodium! That could be a critical error if you're not careful.
Reading a Label for Sodium Content Reading a label for sodium content is never necessary when you're using fresh meat, fresh rice, and fresh vegetables in the food prep process. Substitute cured foods for those that are fresh instead. Skip the ham, bacon, lox, olives, and sauerkraut in favor of fresh veal, pork fish, and eggs.
How to Read a Food Label to Limit Sodium: Care Instructions "Sodium-free" or "salt free" means a serving has less than 5 mg of sodium. "Low-sodium" or "low salt" means a serving has 140 mg or less of sodium. "Reduced-sodium," "lower in salt" or "lower in sodium" means that there is 25% less sodium than what the food normally has. This is still usually too much sodium.
Your Guide to the New Food Label | National Kidney Foundation Sodium Many people with kidney disease must limit their use of sodium. In general, look for foods with no more than 6 to 10% of the daily value for sodium. Keep an eye out for potassium chloride as it is a common ingredient in low sodium products. If listed, be aware that the food will have a high potassium content.
Reading Labels - World Action on Salt & Health Some food labels may only state the sodium content. To convert sodium to salt, you need to multiply the amount by 2.5. For example, 1g of sodium per 100g = 2.5 grams of salt per 100g You then need to know the weight of the serving portion in grams e.g. 30g Then divide the concentration of salt per 100g by 100 and multiply by the serving size.
Sodium: How to Read Food Labels - Intermountain Healthcare Reading food labels can help you monitor how much sodium you are getting in your diet. Here are some of the key parts to check: Notice the serving size Is that the same portion as you are eating? If your serving size increases, then the amount of sodium you eat also increases. This product has 2 servings Saturated Fat 5g per container
Sulfacetamide Sodium-Sulfur Topical: Uses, Side ... - WebMD Find patient medical information for sulfacetamide sodium-sulfur topical on WebMD including its uses, side effects and safety, interactions, pictures, warnings and user ratings.
Don't be salty: Reading food labels can help you lower your sodium ... The researchers estimated sodium intake with 24-hour food recalls. They also asked people about how frequently they ate salty snacks/meals and their frequency of using food labels. The study revealed that people who routinely read food labels ate an average of 93 mg less sodium per day and were less likely to eat salty snacks compared to folks ...
How to Read a Food Label to Limit Sodium: Care Instructions The Nutrition Facts label also gives you the Percent Daily Value for sodium. This is how much of the recommended amount of sodium a serving contains. The daily value for sodium is 2,300 mg. So if the Percent Daily Value says 50%, this means one serving is giving you half of this, or 1,150 mg. Buy low-sodium foods
E number - Wikipedia Commonly found on food labels, their safety assessment and approval are the responsibility of the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). The fact that an additive has an E number implies that its use was at one time permitted in products for sale in the European Single Market ; some of these additives are no longer allowed today.
PDF Controlling Sodium and Reading Labels - Veterans Affairs • Very low sodium: less than 35 milligrams of sodium per serving. • Low sodium: less than 140 milligrams of sodium per serving. 3) Read ingredient lists Labels list the ingredients in order with those that weigh the most appearing first and those that weigh the least appearing last. Choose foods where sodium is listed near the end of the list.
Reading food labels: Tips if you have diabetes - Mayo Clinic Look for foods with fats, cholesterol and sodium on the low end of the Daily Value; keep fiber, vitamins and minerals on the high end. If your doctor or registered dietitian recommends more or less than 2,000 calories a day, you may need to adjust the percentage accordingly — or simply use the percentage as a general frame of reference.
How To Read Food and Beverage Labels - National Institute on Aging Reading food labels can help you make smart food choices. Learn how to read and understand the product date, ingredient list, and Nutrition Facts label. ... Most older adults exceed the recommended limits for saturated fats, sodium, and added sugars. Compare and choose foods to get less than 100% DV of these each day, making sure to adjust for ...
How to Read Labels for a Low Sodium Diet - Salt Sanity Sodium Alginate You may find sodium alginate on the ingredient labels in dairy products like yogurt and ice cream where it's used as a stabilizer. It's used to thicken puddings and jams, prevent moisture loss in meats, and to emulsify salad dressings and beverages. Sodium Citrate
Sodium: Look at the Label Sodium: Look at the Label Over 70% of dietary sodium comes from eating packaged and prepared foods Sodium and Health Diets higher in sodium are associated with an increased risk of developing












Post a Comment for "42 reading labels for sodium"